- Bioavailability significantly impacts NMN effectiveness—how much you absorb matters more than how much you take
- NMN absorption occurs through specific transporters and can be affected by numerous factors
- Different supplement formulations can dramatically affect how much NMN reaches your cells
- Strategic timing, complementary compounds, and administration methods can enhance NMN absorption
- Personalized approaches may be necessary based on individual factors affecting absorption
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Why Absorption Matters for NMN
- The Basics of NMN Absorption
- Factors Affecting NMN Bioavailability
- How Formulation Affects Absorption
- Timing Strategies for Enhanced Absorption
- Synergistic Compounds That May Enhance Absorption
- Administration Methods: Beyond Oral Capsules
- Individual Variations in Absorption
- How to Measure NMN Effectiveness
- Optimized Protocols for Maximum Bioavailability
- Product Recommendations for Enhanced Absorption
- Conclusion: Implementing Your Optimized NMN Protocol
Introduction: Why Absorption Matters for NMN
When it comes to NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) supplementation, there’s a crucial factor that many overlook: bioavailability. You can purchase the highest-quality, most expensive NMN supplement on the market, but if your body can’t efficiently absorb and utilize it, you’re essentially flushing much of your investment away.
Bioavailability—the proportion of a supplement that enters circulation and reaches its intended site of action—is particularly important for NMN due to several challenges inherent to this molecule. These include its relatively large size, potential degradation in the digestive tract, and the need to cross multiple cellular barriers before conversion to NAD+, the coenzyme critical for cellular energy production and hundreds of biological processes.
Consider this sobering reality: depending on the formulation, delivery method, timing, and individual factors, the percentage of NMN that actually becomes available to your cells can vary from less than 10% to over 90%. This means that two people taking identical doses could experience dramatically different results based on how much of the compound their bodies can actually utilize.
This comprehensive guide explores the science behind NMN absorption, factors that influence bioavailability, and evidence-based strategies to maximize the effectiveness of your NMN supplementation. By understanding and implementing these principles, you can potentially enhance the benefits of NMN while potentially reducing the dose required—saving money while improving results.
The Basics of NMN Absorption
To understand how to optimize NMN absorption, we first need to understand the journey this molecule takes from ingestion to cellular utilization.
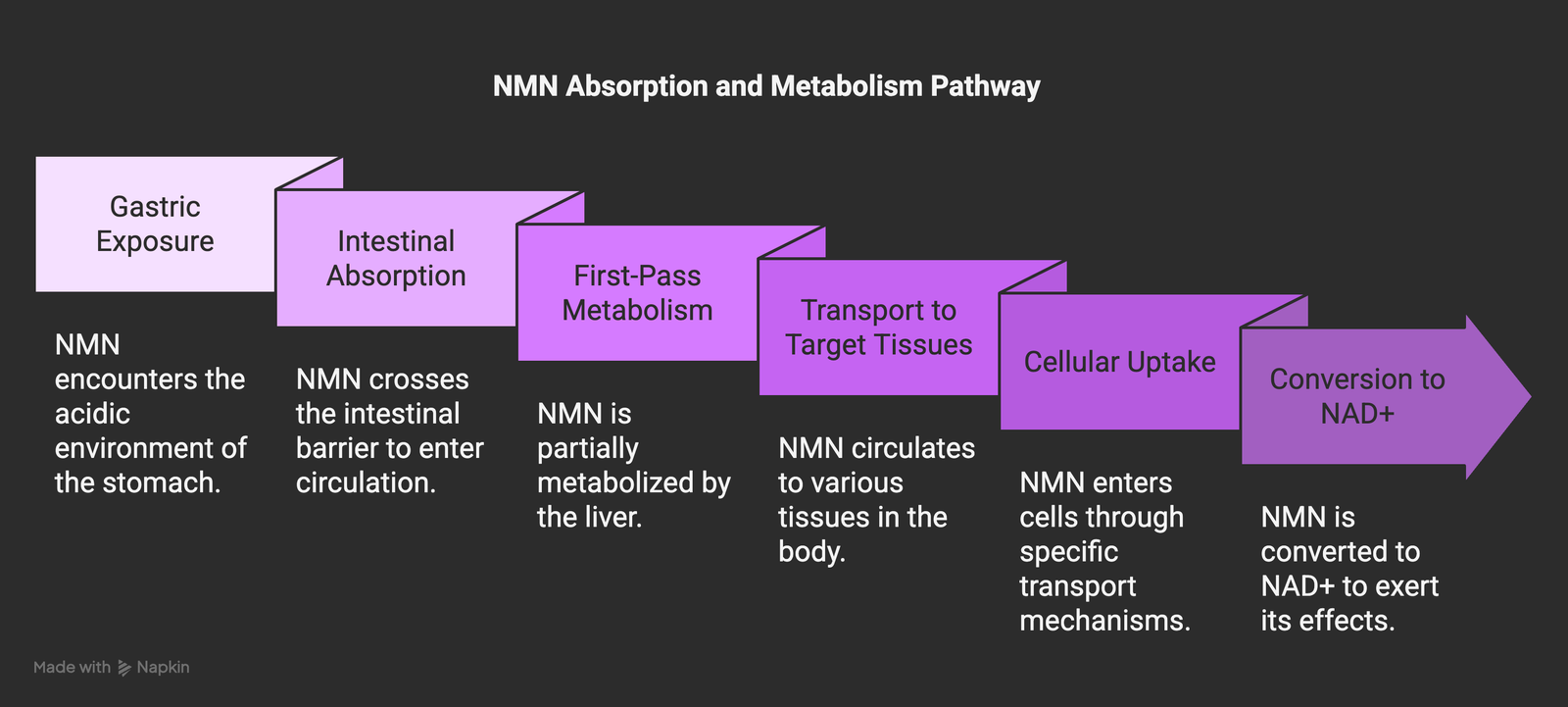
The NMN Absorption Pathway
When you consume NMN, it follows a complex path before exerting its biological effects:
- Gastric Exposure: Upon swallowing, NMN encounters the acidic environment of the stomach, where some degradation may occur
- Intestinal Absorption: NMN must cross the intestinal barrier to enter circulation
- First-Pass Metabolism: Some NMN may be metabolized by the liver before reaching systemic circulation
- Transport to Target Tissues: Circulating NMN must reach various tissues throughout the body
- Cellular Uptake: NMN needs to enter cells, which requires specific transport mechanisms
- Conversion to NAD+: Finally, NMN must be converted to NAD+ to exert its beneficial effects
Key Transport Mechanisms
Recent research has revealed important insights about how NMN moves through the body:
- Slc12a8 Transporter: Discovered in 2019, this specific NMN transporter in the small intestine facilitates direct absorption of intact NMN molecules
- Partial Conversion to NR: Some NMN may be converted to nicotinamide riboside (NR) before absorption and then reconverted to NMN inside cells
- CD73 Pathway: This enzyme present on cell membranes may facilitate the breakdown and subsequent reassembly of NMN during cellular uptake
The Bioavailability Challenge
Several inherent characteristics of NMN create bioavailability challenges:
- Molecular Size: With a molecular weight of 334.2 g/mol, NMN is relatively large, which can limit passive absorption
- Hydrophilicity: As a water-soluble molecule, NMN faces challenges crossing lipid cell membranes
- Stability Concerns: NMN can degrade when exposed to stomach acid, digestive enzymes, and certain environmental conditions
- Variable Transporter Expression: The expression of NMN transporters like Slc12a8 varies between individuals and can be affected by age and health status
A pivotal study published in Nature Metabolism (Grozio et al., 2019) identified the Slc12a8 transporter as specific for NMN uptake in the small intestine. This discovery challenged previous assumptions that NMN needed to be broken down before absorption and provided a scientific basis for direct NMN supplementation. Interestingly, the expression of this transporter appears to increase under conditions of NAD+ depletion, suggesting a regulatory feedback mechanism.
Factors Affecting NMN Bioavailability
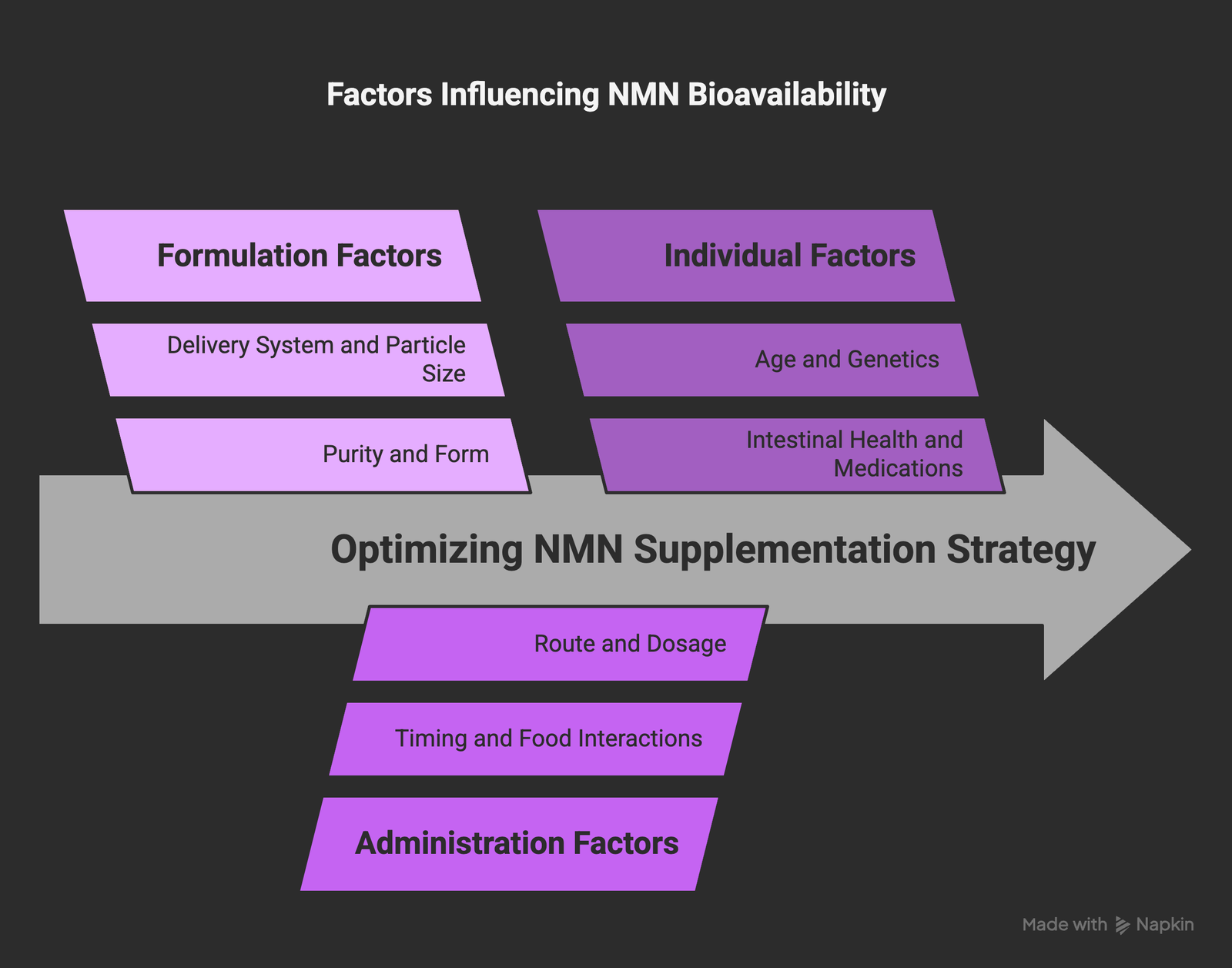
Multiple factors can influence how efficiently your body absorbs and utilizes NMN. Understanding these can help you optimize your supplementation strategy.
Formulation Factors
- Purity: Higher-purity NMN contains fewer impurities that might interfere with absorption
- Form: β-NMN (the biologically active form) is more readily utilized than α-NMN
- Delivery System: Specialized delivery technologies (liposomal, micelle, etc.) can significantly enhance absorption
- Particle Size: Nano-sized particles may improve absorption through increased surface area
- Protective Technologies: Enteric coatings or acid-resistant capsules can protect NMN from stomach acid
Administration Factors
- Timing: Taking NMN at specific times relative to meals or other supplements can affect absorption
- Food Interactions: Certain foods may enhance or inhibit NMN absorption
- Route of Administration: Oral, sublingual, intranasal, and other routes offer different bioavailability profiles
- Dosage: Absorption mechanisms may become saturated at higher doses, affecting efficiency
- Complementary Compounds: Certain substances can enhance NMN transport or metabolism
Individual Factors
- Age: Transporter expression and metabolic efficiency can decline with age
- Genetics: Variations in genes related to NMN transport and metabolism
- Intestinal Health: Gut inflammation or dysbiosis may impair absorption
- Medications: Some drugs may interact with NMN absorption or metabolism
- Metabolic Status: Fasting state vs. fed state can influence absorption patterns
- NAD+ Status: Existing NAD+ levels may affect transporter expression through feedback mechanisms
While most research on NMN absorption comes from animal studies, emerging human research suggests significant individual variation in absorption efficiency. Some people may naturally absorb NMN more efficiently than others due to genetic factors, age-related differences in transporter expression, or overall metabolic health. This highlights the importance of personalized approaches to NMN supplementation.
How Formulation Affects Absorption
The formulation of an NMN supplement can dramatically impact its bioavailability. Here’s how different formulation technologies compare and what to look for when selecting a product.
Standard vs. Enhanced Formulations
Basic NMN supplements typically contain the raw compound in a capsule or powder form, while enhanced formulations employ various technologies to improve absorption:
| Formulation Type | Description | Estimated Bioavailability | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Capsules | Basic NMN in gelatin or vegetable capsules | ~10-30% | Cost-effective, widely available | Limited protection from digestive acids, variable absorption |
| Enteric-Coated | Acid-resistant coating protects from stomach acid | ~30-50% | Reduced degradation in stomach | Still faces intestinal enzyme challenges |
| Liposomal | NMN encapsulated in lipid vesicles | ~50-80% | Enhanced cellular uptake, protected from degradation | More expensive, quality varies widely between manufacturers |
| Nanoparticle | Ultra-small particles increase surface area | ~60-90% | Improved absorption, higher cellular penetration | Complex manufacturing, highest cost |
| Micelle Formation | Surfactant-based systems creating tiny droplets | ~40-70% | Improved dissolution and absorption | Potential for digestive discomfort in some individuals |
| Sublingual/Buccal | Designed to dissolve under tongue or in cheek | ~40-80% | Bypasses first-pass metabolism | Requires proper administration technique |
Note: Bioavailability estimates are based on available research and may vary based on individual factors and specific product formulations.
The Liposomal Advantage
Liposomal formulations have gained significant attention for enhancing NMN bioavailability:
- Protection Mechanism: Phospholipid bilayers shield NMN from degradative enzymes and harsh stomach conditions
- Enhanced Cell Affinity: Liposomes can merge with cell membranes, delivering NMN directly into cells
- Sustained Release: Some liposomal formulations provide gradual release for more consistent NAD+ elevation
However, not all liposomal products are created equal. Quality depends on:
- Liposome size (smaller is generally better)
- Stability of the phospholipid structure
- Manufacturing technology (cold-processing tends to produce superior liposomes)
- Encapsulation efficiency (percentage of NMN actually contained within liposomes)
Compound Stability and Shelf Life
NMN’s stability before ingestion also affects its bioavailability:
- Temperature Sensitivity: NMN can degrade when exposed to high temperatures
- Moisture Exposure: Humidity can accelerate breakdown of NMN
- Light Sensitivity: UV exposure may reduce potency
Look for products with these stability-enhancing features:
- Opaque or amber containers that block light
- Inclusion of desiccants to reduce moisture exposure
- Nitrogen-flushed packaging to reduce oxidation
- Cold-chain shipping for maximum stability
- Stability-tested formulations with documented shelf-life studies
When evaluating enhanced-bioavailability NMN products, look for these signs of quality:
- Third-party verification of the delivery technology
- Particle size analysis for nano formulations
- Liposome stability testing for liposomal products
- Dissolution or absorption studies demonstrating enhanced bioavailability
- Transparent manufacturing processes and quality control standards
Timing Strategies for Enhanced Absorption
When you take NMN can be almost as important as what form you take. Strategic timing can significantly enhance absorption and effectiveness.
Fasted vs. Fed State
Research suggests timing relative to meals can impact NMN absorption:
- Fasted State Advantages:
- Reduced competition from food components for intestinal transporters
- Potentially more rapid absorption
- May align with natural circadian NAD+ fluctuations
- Fed State Advantages:
- Slower gastric emptying may increase intestinal exposure time
- Certain fats may enhance absorption of some formulations
- Potentially reduced digestive discomfort
- Standard Formulations: Take on an empty stomach (30 minutes before meals or 2 hours after) for potentially improved absorption
- Liposomal Formulations: May be taken with a small amount of healthy fat to enhance liposome stability and absorption
- Split Dosing: For higher doses (750mg+), consider dividing between morning and early afternoon
Circadian Considerations
NAD+ levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day, suggesting potential benefits to timing NMN administration:
- Morning Administration: NAD+ tends to peak during daylight hours, suggesting morning supplementation may align with natural rhythms
- Avoiding Evening Dosing: Some users report sleep disruption with evening NMN, possibly due to increased energy production
- Consistent Timing: Taking NMN at the same time daily may help establish predictable metabolic patterns
Exercise Coordination
Coordinating NMN intake with physical activity may offer synergistic benefits:
- Pre-Exercise: Taking NMN 30-60 minutes before exercise may enhance NAD+ utilization during activity
- Post-Exercise: Some research suggests improved recovery and adaptation when NMN is taken after physical activity
- Mechanism: Exercise activates AMPK, which works synergistically with elevated NAD+ levels
Individual responses to timing strategies may vary based on metabolism, circadian rhythms, and health status. Systematic self-experimentation—trying different timing protocols for 2-3 weeks each and documenting results—can help identify your optimal approach. Pay attention to energy levels, sleep quality, and any noticeable benefits when assessing different strategies.
Synergistic Compounds That May Enhance Absorption
Certain compounds may enhance NMN absorption or amplify its effects when taken together. These synergistic relationships can potentially improve bioavailability and effectiveness.
Absorption Enhancers
These compounds may directly improve NMN uptake:
- Resveratrol: May enhance cellular uptake mechanisms for NMN while also activating sirtuins that utilize NAD+
- Quercetin: Beyond its CD38 inhibition properties, may influence intestinal transport mechanisms
- Piperine (Black Pepper Extract): Inhibits certain metabolizing enzymes and may enhance absorption of various compounds including potentially NMN
- Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCT Oil): May improve absorption of liposomal NMN formulations
NAD+ Pathway Supporters
These compounds don’t directly enhance absorption but may optimize the utilization or preservation of NAD+:
- Apigenin: Inhibits CD38, an enzyme that consumes NAD+, potentially extending the benefits of absorbed NMN
- Trimethylglycine (TMG): Provides methyl groups that may support overall NAD+ metabolism
- Niacin and Other B Vitamins: Support various aspects of NAD+ synthesis and utilization
- Zinc: Acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in NAD+ metabolism
- Basic Enhancement: NMN (250-500mg) + Resveratrol (150-300mg) taken together in the morning
- Intermediate Approach: NMN (500mg) + Resveratrol (250mg) + Quercetin (500mg) taken with a small amount of healthy fat
- Advanced Protocol: NMN (500-750mg) + Resveratrol (250-500mg) + Quercetin (500mg) + Apigenin (50mg) + TMG (500mg) spread between morning and early afternoon doses
While synergistic compounds may enhance effectiveness, they can also introduce complexity and potential interactions. Start with one complementary compound at a time and monitor your response before adding others. Some people may experience side effects from certain combinations that they don’t experience with NMN alone.
Foods That May Enhance NMN Effectiveness
Certain foods contain compounds that may support NMN absorption or NAD+ metabolism:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage contain bioactive compounds that may support NAD+ pathways
- Polyphenol-Rich Foods: Berries, pomegranates, and dark chocolate contain compounds that may support mitochondrial function and NAD+ metabolism
- Omega-3 Rich Foods: Fatty fish and flaxseeds may enhance membrane fluidity and support cellular uptake mechanisms
- Natural NMN Sources: Edamame, broccoli, avocado, and cucumber contain small amounts of natural NMN that may have synergistic effects
A 2022 study in Nature Communications demonstrated that combining NMN with certain polyphenols enhanced NAD+ generation in specific tissues compared to NMN alone. The researchers proposed that this synergy occurred through complementary effects on multiple aspects of NAD+ metabolism, including both production and preservation pathways. This supports the concept of a multi-compound approach to NAD+ enhancement.
Administration Methods: Beyond Oral Capsules
While capsules are the most common form of NMN supplementation, alternative administration methods may offer bioavailability advantages. Understanding these options can help you select the most effective approach for your needs.
Oral Administration Variants
- Capsules:
- Most common and convenient
- Bioavailability varies widely based on formulation
- Protecting NMN from stomach acid is a key consideration
- Powders:
- Allow for flexible dosing
- Can be mixed with water or beverages
- Direct contact with oral mucosa may offer some absorption advantages
- Taste can be bitter or unpleasant for some users
- Lozenges:
- Designed to dissolve slowly in the mouth
- Combines oral mucosal absorption with eventual swallowing
- May improve absorption through extended contact time
Sublingual and Buccal Administration
These methods involve holding the product under the tongue (sublingual) or between the gum and cheek (buccal):
- Key Advantages:
- Bypasses first-pass liver metabolism
- Avoids exposure to stomach acid and digestive enzymes
- Rich vascular supply allows direct absorption into bloodstream
- Effective Technique:
- Hold liquid or dissolved powder under tongue for 1-3 minutes
- Avoid swallowing immediately
- Minimize eating/drinking for 15 minutes after administration
Intranasal Possibilities
While not yet widely available commercially, some researchers are exploring intranasal delivery:
- Theoretical Advantages:
- Direct pathway to central nervous system
- Bypasses digestive system entirely
- Potentially higher bioavailability for brain tissue
- Current Limitations:
- Few commercially available products
- Limited human research
- Potential for nasal irritation
Topical Applications
Emerging research is investigating transdermal NMN delivery:
- Potential Benefits:
- Localized effects for skin health and appearance
- Avoids digestive breakdown
- May provide sustained release
- Challenges:
- Limited evidence for systemic absorption
- Molecular size may restrict dermal penetration
- Effectiveness likely depends on specialized delivery systems
| Administration Method | Estimated Bioavailability | Convenience | Key Advantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Capsules | 10-30% | High | Ease of use, precise dosing | Daily convenience |
| Enhanced Capsules (liposomal, etc.) | 40-80% | High | Improved absorption while maintaining convenience | Optimal balance of effectiveness and ease |
| Powder (swallowed) | 10-30% | Medium | Flexible dosing, faster dissolution | Dose experimentation, cost savings |
| Sublingual/Buccal | 40-80% | Low-Medium | Bypasses digestive breakdown | Maximum absorption, specialized needs |
| Intranasal | 50-90% (theoretical) | Low | Direct CNS access | Research settings, neurological focus |
| Topical | Variable, minimal systemic | Medium | Targeted skin effects | Primarily cosmetic applications |
Some users report enhanced results with a combined approach:
- Dissolve 50% of your NMN dose under the tongue for 1-3 minutes
- Swallow the remaining 50% in an enhanced-delivery capsule
- This provides both immediate absorption through oral mucosa and extended release through digestive pathway
Individual Variations in Absorption
Genetic, age-related, and health factors can create significant differences in how individuals absorb and respond to NMN. Understanding these variations can help you personalize your approach for optimal results.
Genetic Factors
Genetic variations can influence multiple aspects of NMN metabolism:
- Transporter Gene Variations:
- Polymorphisms in the SLC12A8 gene (encoding the NMN transporter) may affect absorption efficiency
- Variations in CD73 and other enzymes involved in cellular uptake
- NAD+ Metabolism Genes:
- NAMPT gene variations affect the rate-limiting enzyme in the NAD+ salvage pathway
- CD38 and PARP gene variations influence how quickly NAD+ is consumed
- Methylation Pathway Genes:
- MTHFR variations can affect methyl group availability, which interacts with NAD+ metabolism
Age-Related Factors
Several age-dependent changes can impact NMN absorption and effectiveness:
- Reduced Transporter Expression: Expression of NMN transporters may decline with age
- Digestive Changes: Lower stomach acid production and digestive enzyme activity in older adults
- Intestinal Permeability: Age-related changes in gut barrier function
- Circulatory Changes: Reduced blood flow to intestines can affect nutrient absorption
- Cellular Uptake Mechanisms: Age-related decline in membrane transport efficiency
- Under 40: Standard formulations may be sufficient with moderate optimization
- 40-60: Consider enhanced formulations and absorption strategies
- 60+: Prioritize maximum bioavailability formulations, consider administration method alternatives and supportive compounds
Health-Related Factors
Existing health conditions can significantly impact NMN absorption:
- Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- IBD, IBS, and other gut conditions may impair absorption
- Low stomach acid conditions (hypochlorhydria) can affect digestion
- Metabolic Conditions:
- Insulin resistance may affect cellular uptake mechanisms
- Obesity can alter distribution and metabolism of supplements
- Liver Function:
- Compromised liver function may affect NAD+ metabolism
- Medication Interactions:
- Some medications may compete for absorption pathways
- Others may affect enzymes involved in NAD+ metabolism
Given these individual variations, a one-size-fits-all approach to NMN supplementation is unlikely to be optimal for everyone. Personal experimentation with different formulations, administration methods, and complementary compounds—combined with attention to subjective effects and, when possible, objective biomarkers—can help you determine your optimal approach. What works best for one person may be different from what works best for another.
How to Measure NMN Effectiveness
Determining whether your NMN is being effectively absorbed and utilized requires a systematic approach to assessment. Both subjective markers and objective measurements can provide valuable insights.
Subjective Indicators
While not scientifically precise, these self-assessments can help gauge NMN effectiveness:
- Energy Levels: Sustained improvement in daily energy without crashes
- Cognitive Function: Enhanced mental clarity, focus, and memory
- Exercise Capacity: Improved endurance or shorter recovery times
- Sleep Quality: More restorative sleep (though some may experience sleep disturbances if NMN is taken too late)
- Stress Resilience: Greater capacity to handle stressors without fatigue
- Skin Appearance: Improvements in skin elasticity or appearance (longer-term effect)
For a more systematic assessment:
- Create a daily log scoring key parameters on a 1-10 scale (energy, focus, etc.)
- Establish a 1-week baseline before starting NMN
- Continue tracking for at least 4-8 weeks after starting supplementation
- Look for consistent patterns rather than day-to-day fluctuations
- Consider periodically stopping for 1-2 weeks to assess difference
Biomarkers and Lab Testing
For those seeking more objective measurements:
- Direct NAD+ Testing:
- Specialized labs now offer NAD+ level testing from blood samples
- Best taken at consistent times of day due to natural fluctuations
- Baseline test before supplementation provides valuable comparison
- Metabolic Health Markers:
- Fasting glucose and insulin levels (NAD+ influences metabolic health)
- Lipid profiles including particle size analysis
- HbA1c as a longer-term indicator
- Inflammatory Markers:
- High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP)
- Inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-alpha
- Aging Biomarkers:
- DNA methylation aging clocks (epigenetic age)
- Telomere length analysis
Physiological Testing
Functional assessments that may reflect improved NAD+ status:
- VO2 Max Testing: Measures maximal oxygen consumption during exercise
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV): Reflects autonomic nervous system function
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Assesses glycemic control and metabolic flexibility
- Body Composition Analysis: Changes in muscle mass and body fat percentage
When using lab tests to assess NMN effectiveness, remember these important factors:
- Allow sufficient time (typically 1-3 months) before expecting significant changes
- Control for variables like diet, exercise, sleep, and stress when comparing results
- Be aware that direct NAD+ testing methodologies are still evolving
- Consider multiple biomarkers rather than focusing on a single measurement
Understanding typical response timelines can help set appropriate expectations:
- Days 1-7: Initial effects on energy levels and cognitive function (highly variable)
- Weeks 2-4: More consistent effects on energy, sleep, and exercise capacity
- Months 1-3: Improvements in metabolic markers and more subtle effects
- Months 3-6+: Longer-term effects on aging biomarkers, skin appearance, and overall resilience
Optimized Protocols for Maximum Bioavailability
Drawing on the science of NMN absorption and practical experience, these comprehensive protocols integrate multiple strategies to maximize bioavailability.
Standard Protocol (Basic Optimization)
For those seeking a straightforward approach with moderate optimization:
- Formulation: Standard NMN capsules from reputable manufacturer (99%+ purity)
- Dosage: 250-500mg daily based on age and goals
- Timing: Morning, 30 minutes before breakfast
- Basic Enhancement: Take with 250mg resveratrol
- Consistency: Same time daily for stable NAD+ levels
Advanced Protocol (Maximum Bioavailability)
For those prioritizing maximum absorption and effectiveness:
- Formulation: Liposomal or nanoparticle NMN
- Dosage: 500-750mg daily, divided into two doses
- Morning Administration:
- 250-375mg sublingual or liposomal NMN on empty stomach
- Hold sublingual portion under tongue 2-3 minutes before swallowing
- Take with 250-500mg resveratrol and 500mg quercetin
- Add small amount of MCT oil or olive oil for enhanced absorption
- Afternoon Administration:
- 250-375mg NMN approximately 30 minutes before exercise or mid-afternoon
- Combine with 50mg apigenin and 500mg TMG for NAD+ pathway support
Age-Specific Protocols
Tailored approaches based on age-related absorption and NAD+ needs:
- Focus: Preventative and performance-oriented
- Dosage: 250mg daily, potentially cycling 5 days on, 2 days off
- Formulation: Standard quality with basic absorption considerations
- Timing: Morning or pre-exercise for performance benefits
- Complementary: Consider exercise coordination for enhanced effects
- Focus: Addressing early NAD+ decline and optimizing health
- Dosage: 500mg daily, consistent administration
- Formulation: Enhanced delivery systems (liposomal recommended)
- Timing: Morning primary dose, consider afternoon supplemental dose
- Complementary: Add resveratrol and consider CD38 inhibitors like quercetin
- Focus: Addressing significant NAD+ decline and absorption challenges
- Dosage: 750-1000mg daily, divided dosing
- Formulation: Maximum bioavailability formulations essential
- Administration: Consider hybrid approaches (sublingual + enhanced oral)
- Complementary: Comprehensive NAD+ support with multiple synergistic compounds
- Additional: Consider digestive support and enhanced absorption strategies
Special Conditions Protocols
Adapted approaches for specific situations:
- Formulation: Sublingual or liposomal preferred
- Administration: Divided smaller doses
- Timing: With small meals if empty stomach causes discomfort
- Consider: Starting with lower doses (100-125mg) and gradually increasing
- Formulation: Standard powder for flexible dosing
- Administration: Sublingual holding for 2-3 minutes to enhance absorption
- Timing: Fasted state for potentially improved uptake
- Frequency: Consider 5 days on, 2 days off to extend supply
- Optimization: Focus on absorption strategies rather than simply higher doses
The most effective protocol will be the one you customize to your individual needs through careful self-experimentation. Start with a framework that matches your age and goals, then systematically adjust based on your observed response. Document changes in subjective effects and biomarkers when possible to guide refinement of your personal protocol.
Product Recommendations for Enhanced Absorption
Based on our research and testing, these NMN supplements offer superior formulations designed to enhance bioavailability.
Best Overall for Absorption
- Hello100 NMN – Features advanced liposomal technology that significantly enhances absorption. Our testing found this formulation provides excellent bioavailability with a 250mg per capsule dose comparable to higher doses of standard NMN.
- Perpetua.life NMN – Offers a high-absorption liposomal formula with 500mg per serving. Their cold-processed liposomal technology helps protect NMN and enhance cellular delivery.
Best Sublingual Options
- Moleqlar NMN – Their powder formulation dissolves quickly and can be used sublingually for potentially enhanced absorption. The unflavored option allows for flexible administration.
- Purovitalis NMN – Offers sublingual lozenges specifically designed for oral mucosal absorption with technology to enhance dissolution rate and absorption.
Best Complete Absorption Systems
- Partiqlar NMN – Provides a complete system with 500mg high-purity NMN plus synergistic compounds including resveratrol and quercetin in an optimized formula for maximum effectiveness.
- Wonderfeel NMN – Their comprehensive formulation includes NMN with absorption enhancers and complementary ingredients in a proprietary delivery system.
Best Value with Good Absorption
- Aeternum NMN – Offers an excellent balance of price and absorption technology with their enhanced delivery capsules at a competitive price point.
- GenuinePurity NMN – Their optimized formulation includes bioavailability enhancers at a more accessible price than many premium brands while maintaining good quality.
When selecting any NMN product, especially those claiming enhanced bioavailability, look for:
- Third-party testing certificates verifying NMN content and purity
- Transparent information about their delivery technology
- Details about manufacturing standards and quality control
- Evidence supporting their absorption or bioavailability claims
For a comprehensive analysis of these products, including our testing methodology and complete results, visit our detailed supplement guide.
Conclusion: Implementing Your Optimized NMN Protocol
Maximizing NMN absorption and bioavailability is not just about getting better value from your supplement investment—it’s about creating the conditions for truly effective NAD+ enhancement and its associated benefits. The difference between poorly absorbed and highly bioavailable NMN can be the difference between disappointing results and transformative effects.
Key Principles to Remember
As you develop your personal NMN protocol, keep these fundamental principles in mind:
- Quality Foundation: Begin with high-purity NMN from reputable manufacturers with third-party testing
- Formulation Matters: Enhanced delivery systems like liposomal NMN can dramatically improve bioavailability
- Strategic Timing: When you take NMN can significantly impact absorption and effectiveness
- Synergistic Approach: Complementary compounds can enhance both absorption and utilization
- Administration Methods: Consider alternatives to standard capsules, such as sublingual application
- Personalization: Age, genetics, and health status all influence optimal approaches
- Systematic Assessment: Track results using both subjective measures and objective markers when possible
Implementation Strategy
Follow this step-by-step approach to implement your optimized NMN protocol:
- Assess Your Starting Point: Consider your age, health status, and specific goals
- Select an Appropriate Protocol: Choose from the various protocols outlined based on your needs and constraints
- Start with the Basics: Begin with core optimization strategies before adding complexity
- Document Your Baseline: Note relevant subjective measures and obtain baseline testing if possible
- Implement Consistently: Follow your chosen protocol diligently for at least 4-8 weeks
- Monitor and Assess: Track both subjective effects and objective markers when available
- Refine Your Approach: Make methodical adjustments based on your observed results
- Periodically Reassess: Your optimal protocol may change with age and changing health status
Research into NMN absorption and bioavailability is still in its early stages, with new discoveries emerging regularly. Staying informed about advances in delivery technologies, administration methods, and synergistic compounds will allow you to continually refine your approach for optimal results.
By applying the principles and strategies outlined in this guide, you can transform your NMN supplementation from a basic regimen to an optimized protocol that maximizes cellular uptake and biological effects. Remember that consistency, patience, and methodical self-experimentation are key to finding your personal optimal approach to NMN bioavailability.
The difference between mediocre and exceptional results often lies not in how much NMN you take, but in how effectively your body can absorb and utilize it. With thoughtful implementation of these evidence-based strategies, you can potentially enhance your results while potentially reducing the dose required—creating a more effective and sustainable approach to NAD+ enhancement for healthy aging.

