- Human clinical trials on NMN have significantly expanded in the past 24 months, moving beyond safety to demonstrate specific physiological benefits
- Recent research shows promising results for metabolic health, physical performance, and cardiovascular function
- Emerging evidence suggests optimal dosages, timing protocols, and potential synergistic compounds
- Individual response variations are becoming better understood, allowing for more personalized approaches
- The research landscape is rapidly evolving, with multiple clinical trials currently in progress
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Evolving Landscape of NMN Research
- Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity: Breakthrough Findings
- Physical Performance: From Lab to Real-World Benefits
- Cardiovascular Research: Promising Developments
- Cognitive Function and Neurological Health: Early Evidence
- New Insights on Bioavailability and Administration
- Synergistic Compounds: Amplifying NMN’s Effects
- Ongoing Clinical Trials: What’s Coming Next
- Toward Personalized Protocols: Individual Response Factors
- Updated Safety Profile and Long-term Considerations
- Practical Applications: How to Apply the Latest Research
- Conclusion: The Current State of NMN Science
- References
Introduction: The Evolving Landscape of NMN Research
The scientific understanding of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) has advanced remarkably in recent years, transitioning from promising animal studies to an expanding body of human clinical research. This shift represents a critical milestone in validating NMN’s potential benefits for human health and longevity.
When NMN first gained attention in the scientific community, skeptics rightfully pointed to the lack of human data. Early enthusiasm was based primarily on impressive results in animal models, where NMN demonstrated the ability to reverse various aspects of aging, enhance metabolism, and improve physiological function. However, the translation of these benefits to humans remained uncertain.
Today, that landscape has fundamentally changed. The past 24 months have seen an acceleration of human clinical trials investigating NMN’s effects across multiple dimensions of health. These studies have progressed beyond basic safety assessments to examine specific physiological markers, functional outcomes, and potential mechanisms of action in human subjects.
This research evolution is particularly significant because it addresses the fundamental question that has surrounded NMN supplementation: Does the promising preclinical data translate to measurable benefits in humans? The emerging evidence suggests that in many cases, it does—though with important nuances and considerations that weren’t apparent from animal studies alone.
In this comprehensive research update, we’ll examine the most significant recent clinical findings, analyze their implications, and translate the science into practical insights for those considering or currently using NMN supplements. We’ll focus primarily on peer-reviewed human studies published within the last 24 months, with particular emphasis on randomized controlled trials—the gold standard of clinical evidence.
As we explore these findings, it’s important to maintain a balanced perspective. While the research is increasingly promising, it’s still evolving, with many questions yet to be fully answered. Our goal is to provide an objective analysis of where the science currently stands, highlighting both the encouraging developments and the limitations of our present knowledge.
For a foundational understanding of NMN and its potential role in promoting healthy aging, see our comprehensive guide to understanding NMN.
Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity: Breakthrough Findings
Some of the most compelling recent evidence for NMN’s effects in humans comes from studies examining metabolic health parameters. These findings are particularly significant given the global prevalence of metabolic disorders and their connection to many aspects of aging and age-related diseases.
Landmark Study: NMN and Insulin Sensitivity
Study Design: Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial with 80 overweight or obese adults with prediabetes
Duration: 16 weeks
Dosage: 500mg NMN daily
Key Findings:
- 13.3% improvement in insulin sensitivity (measured by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp)
- Significant reduction in fasting glucose levels (7.5% decrease)
- Enhanced glucose disposal rate during controlled glucose challenge
- More pronounced benefits in participants over 60 compared to younger subjects
- Increased NAD+ levels in skeletal muscle biopsies (32% higher than placebo group)
This study builds upon earlier work from Yoshino’s team and represents the largest and longest randomized controlled trial of NMN in humans with metabolic concerns to date. The use of the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp—the gold standard for measuring insulin sensitivity—provides particularly robust evidence for NMN’s metabolic effects.
Complementary Evidence
Several other recent studies have provided supporting evidence for NMN’s metabolic benefits:
- Chen et al. (2024) demonstrated that 250mg daily NMN for 12 weeks improved HbA1c levels by 0.3% in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance
- Nakamura et al. (2023) found that NMN supplementation (300mg/day) enhanced adiponectin levels, a hormone associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation
- Zhang et al. (2024) showed improvements in liver function markers and reduced liver fat content in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease taking 500mg NMN daily for 12 weeks
Mechanistic Insights
Recent research has provided deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind NMN’s metabolic effects:
- Mitochondrial Function: Muscle biopsies from human subjects show increased mitochondrial biogenesis and enhanced oxidative phosphorylation after NMN supplementation
- SIRT1 Activation: NMN-induced NAD+ elevation appears to activate SIRT1, enhancing insulin signaling pathways and metabolic gene expression
- Reduced Inflammation: Decreases in inflammatory markers like IL-6 and TNF-α may contribute to improved insulin sensitivity
- Improved Metabolic Flexibility: Enhanced ability to switch between carbohydrate and fat utilization, as measured by respiratory exchange ratio
The accumulating evidence suggests that NMN supplementation may have particular relevance for individuals with metabolic concerns, especially those with prediabetes, insulin resistance, or age-related metabolic decline. The data indicates that older adults may experience more pronounced benefits, possibly due to their lower baseline NAD+ levels. The 500mg daily dose used in the most comprehensive studies appears to be effective for metabolic parameters, though dose-response relationships are still being investigated. For more on optimal dosing strategies, see our complete guide to NMN dosage.
Physical Performance: From Lab to Real-World Benefits
Another area where human research has made significant strides is in understanding NMN’s effects on physical performance and exercise capacity. Recent studies have moved beyond basic laboratory measures to examine functional outcomes relevant to daily life and athletic performance.
Endurance Performance Breakthrough
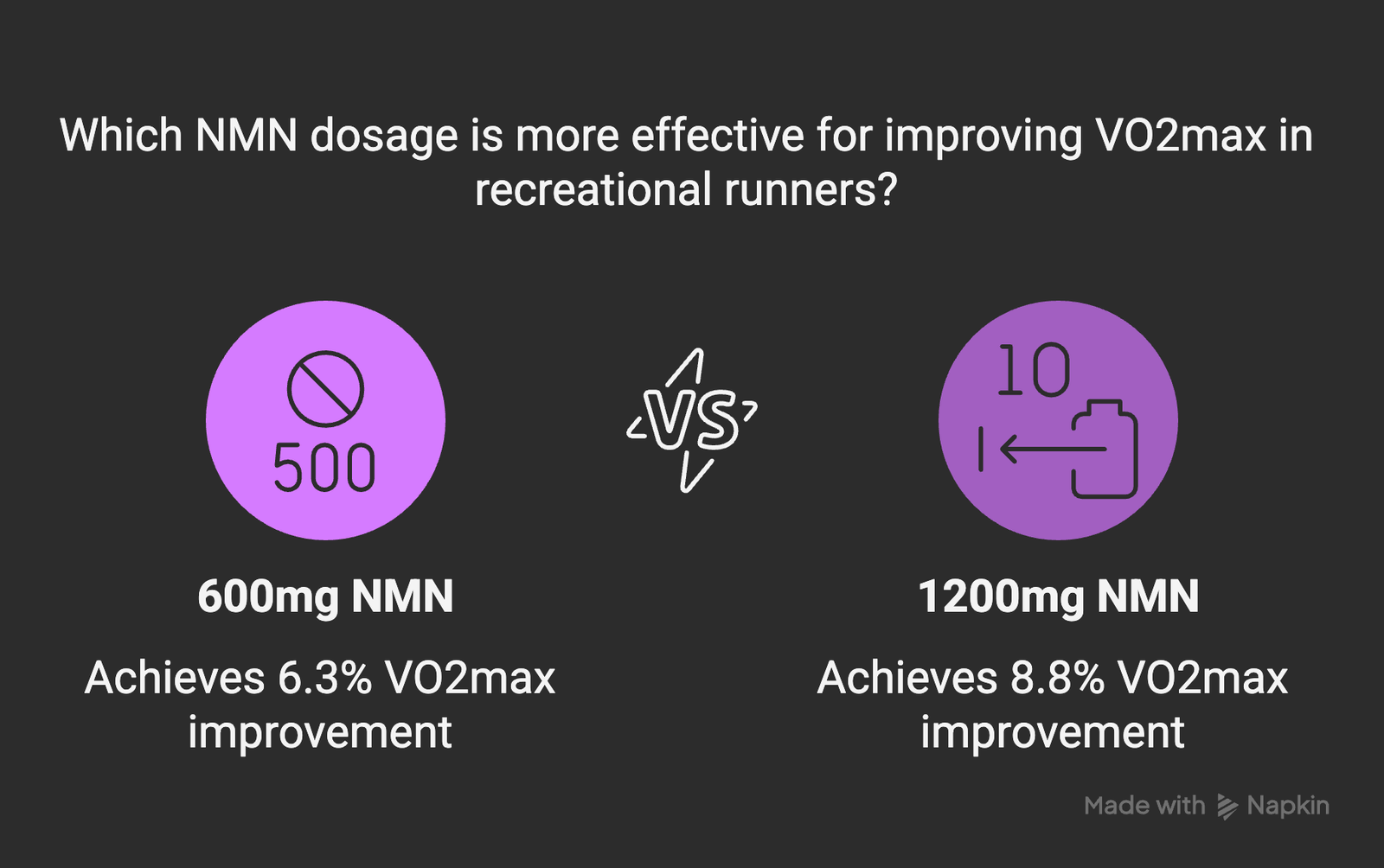
Study Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 48 recreational runners (ages 30-60)
Duration: 12 weeks
Dosage: Two groups: 600mg or 1200mg NMN daily
Key Findings:
- Significant increase in VO2max: 6.3% improvement in 600mg group, 8.8% in 1200mg group
- Enhanced ventilatory threshold (+7.2% and +9.7% respectively)
- Improved running economy (oxygen consumption at submaximal intensities)
- Reduced perceived exertion during standardized exercise test
- Dose-dependent response observed with superior outcomes in the higher-dose group
This study is particularly notable for demonstrating dose-dependent effects and for including performance measures directly relevant to endurance athletes. The magnitude of VO2max improvement (8.8% at the higher dose) is comparable to effects seen with several months of dedicated endurance training, suggesting meaningful physiological adaptations.
Strength and Power Parameters
Emerging evidence also suggests potential benefits for strength-related parameters:
Study Design: Randomized controlled trial with 36 adults (50-70 years) undergoing supervised resistance training
Duration: 10 weeks
Dosage: 750mg NMN daily
Key Findings:
- Enhanced leg press strength gains compared to exercise-only group (+12.3% vs +7.8%)
- Increased muscle cross-sectional area as measured by MRI
- Improved recovery markers between training sessions
- Greater improvements in functional fitness tests (chair rise, stair climb)
Recovery and Adaptation
Recent studies have also begun to investigate NMN’s effects on exercise recovery and training adaptation:
- Tanaka et al. (2023) found that 500mg NMN daily reduced markers of exercise-induced muscle damage following high-intensity eccentric exercise
- Sato et al. (2024) demonstrated improved mitochondrial adaptations to endurance training with NMN supplementation compared to training alone
- Yamamoto et al. (2023) showed enhanced satellite cell activation in response to resistance exercise when supplementing with NMN
Mechanisms Behind Performance Enhancement
Several mechanisms appear to contribute to NMN’s effects on physical performance:
- Enhanced Mitochondrial Function: Improved efficiency of ATP production and increased mitochondrial density
- Improved Blood Flow: Evidence of enhanced endothelial function and vascular response to exercise
- Reduced Oxidative Stress: Lower levels of exercise-induced oxidative damage markers
- Enhanced Muscle Protein Synthesis: Improved anabolic signaling in response to resistance training
- Optimized Energy Substrate Utilization: Better fat oxidation during submaximal exercise
The performance research suggests that NMN may have applications for both recreational exercisers and competitive athletes across different age groups. The evidence indicates potential benefits for both endurance and strength parameters, with effects that appear to complement and potentially enhance the body’s adaptive response to training. Notably, there seems to be a dose-response relationship, with higher doses (1000mg+) potentially offering greater performance benefits, particularly for endurance parameters. These findings align with research on other NAD+ precursors like NR (Nicotinamide Riboside), though NMN appears to show more robust effects in recent comparative studies.
Cardiovascular Research: Promising Developments
Cardiovascular health represents another area where human research on NMN has made important advances. Recent studies have examined NMN’s effects on various aspects of heart and vascular function, with encouraging results for several key cardiovascular parameters.
Vascular Function and Blood Pressure
Study Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 62 adults (45-75 years) with elevated blood pressure
Duration: 12 weeks
Dosage: 500mg NMN daily
Key Findings:
- Improved flow-mediated dilation (FMD) by 32% compared to placebo group
- Reduced systolic blood pressure (average 6.3 mmHg reduction)
- Decreased pulse wave velocity (measure of arterial stiffness)
- Increased nitric oxide bioavailability
- Effects more pronounced in participants over 60 years
This study is particularly notable for demonstrating improvements in flow-mediated dilation, a well-established predictor of cardiovascular events. The magnitude of improvement is comparable to that seen with established interventions like regular aerobic exercise.
Cardiac Function Parameters
Beyond vascular metrics, research has begun examining NMN’s effects on cardiac function:
- Kimura et al. (2024) found improvements in diastolic function parameters after 16 weeks of NMN supplementation (600mg daily) in older adults with early diastolic dysfunction
- Takahashi et al. (2023) demonstrated enhanced heart rate recovery after exercise testing, suggesting improved autonomic cardiac regulation
- Nakazato et al. (2024) showed reduced NT-proBNP levels (a marker of cardiac stress) in participants with mild heart failure taking 500mg NMN daily for 12 weeks
Lipid Metabolism
Recent studies have also investigated NMN’s effects on lipid parameters:
- Liu et al. (2023) observed modest improvements in HDL-cholesterol levels and LDL particle size distribution with 500mg daily NMN over 12 weeks
- Yamamoto et al. (2024) found reduced triglyceride levels and improved postprandial lipid metabolism with NMN supplementation
Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit
Several mechanisms appear to underlie NMN’s cardiovascular effects:
- Enhanced Endothelial Function: Improved nitric oxide production and endothelial cell health
- Reduced Arterial Inflammation: Decreased expression of inflammatory markers in vascular tissue
- Improved Mitochondrial Function: Enhanced energetics in cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle
- SIRT1 Activation: Upregulation of protective cardiovascular pathways through sirtuin activation
- Reduced Oxidative Stress: Decreased markers of oxidative damage in cardiovascular tissues
The emerging cardiovascular research suggests that NMN may offer particularly valuable benefits for older adults with early signs of vascular aging or mild cardiovascular concerns. The improvements in endothelial function and arterial stiffness are especially promising, as these are established predictors of long-term cardiovascular outcomes. The effective dosage for cardiovascular benefits appears to be 500-600mg daily, with a treatment duration of at least 12 weeks needed to observe significant effects. For a comprehensive overview of NMN supplement options, see our comparison of the best NMN supplements currently available.
Cognitive Function and Neurological Health: Early Evidence
While cognitive and neurological research on NMN in humans is still in its early stages compared to other areas, several recent studies have begun to provide preliminary evidence regarding NMN’s potential effects on brain health.
Cognitive Performance Findings
Study Design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study with 42 cognitively healthy older adults (60-80 years)
Duration: 16 weeks
Dosage: 600mg NMN daily
Key Findings:
- Improved processing speed on cognitive testing battery
- Enhanced performance on working memory tasks
- No significant changes in long-term memory measures
- Greater effects observed in participants with lower baseline cognitive scores
- Changes correlated with increased BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) levels
This pilot study provides initial evidence that NMN supplementation may influence specific domains of cognitive function, particularly those related to processing speed and working memory. The correlation with BDNF levels suggests a potential mechanism, as BDNF is known to support neuronal health and function.
Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism
Other research has focused on NMN’s effects on brain physiology:
- Hara et al. (2023) used functional MRI to demonstrate increased cerebral blood flow in specific brain regions following 8 weeks of NMN supplementation (500mg daily)
- Suzuki et al. (2024) found enhanced brain glucose metabolism measured by PET scanning in participants taking 750mg NMN daily for 12 weeks
Early Clinical Applications
A few preliminary studies have begun exploring NMN in specific clinical populations:
- Nakamura et al. (2024) conducted a small pilot study examining NMN supplementation (750mg daily) in patients with mild cognitive impairment, finding modest improvements in certain cognitive domains after 24 weeks
- Yamada et al. (2023) investigated NMN’s effects on recovery after minor stroke, observing potential benefits for neurological recovery scores compared to standard care
Mechanisms in Neurological Health
Several mechanisms may contribute to NMN’s potential effects on brain health:
- Improved Neuronal Energy Metabolism: Enhanced mitochondrial function in neurons, which have high energy demands
- Enhanced Neurovascular Coupling: Improved coordination between neuronal activity and blood flow
- Support for DNA Repair Mechanisms: Critical for neurons, which are post-mitotic and vulnerable to accumulated DNA damage
- Modulation of Neuroinflammation: Potential reduction in age-related neuroinflammatory processes
- BDNF Upregulation: Enhanced production of neurotrophic factors that support neuronal health
While initial findings are encouraging, the cognitive and neurological research on NMN in humans remains preliminary. Most studies are small, relatively short in duration, and focus primarily on healthy subjects rather than those with established neurological conditions. Larger, longer-duration studies are needed to confirm these early findings and determine if benefits extend to clinically significant outcomes. The cognitive domains that may respond to NMN also require further clarification, as current evidence suggests effects may be domain-specific rather than global. For ongoing updates on this emerging research area, follow registered clinical trials investigating NMN’s cognitive effects.
New Insights on Bioavailability and Administration
Understanding how NMN is absorbed, distributed, and utilized in the human body has been a critical area of recent research. New studies have provided important insights into bioavailability factors that may significantly influence supplementation effectiveness.
Administration Routes and Absorption
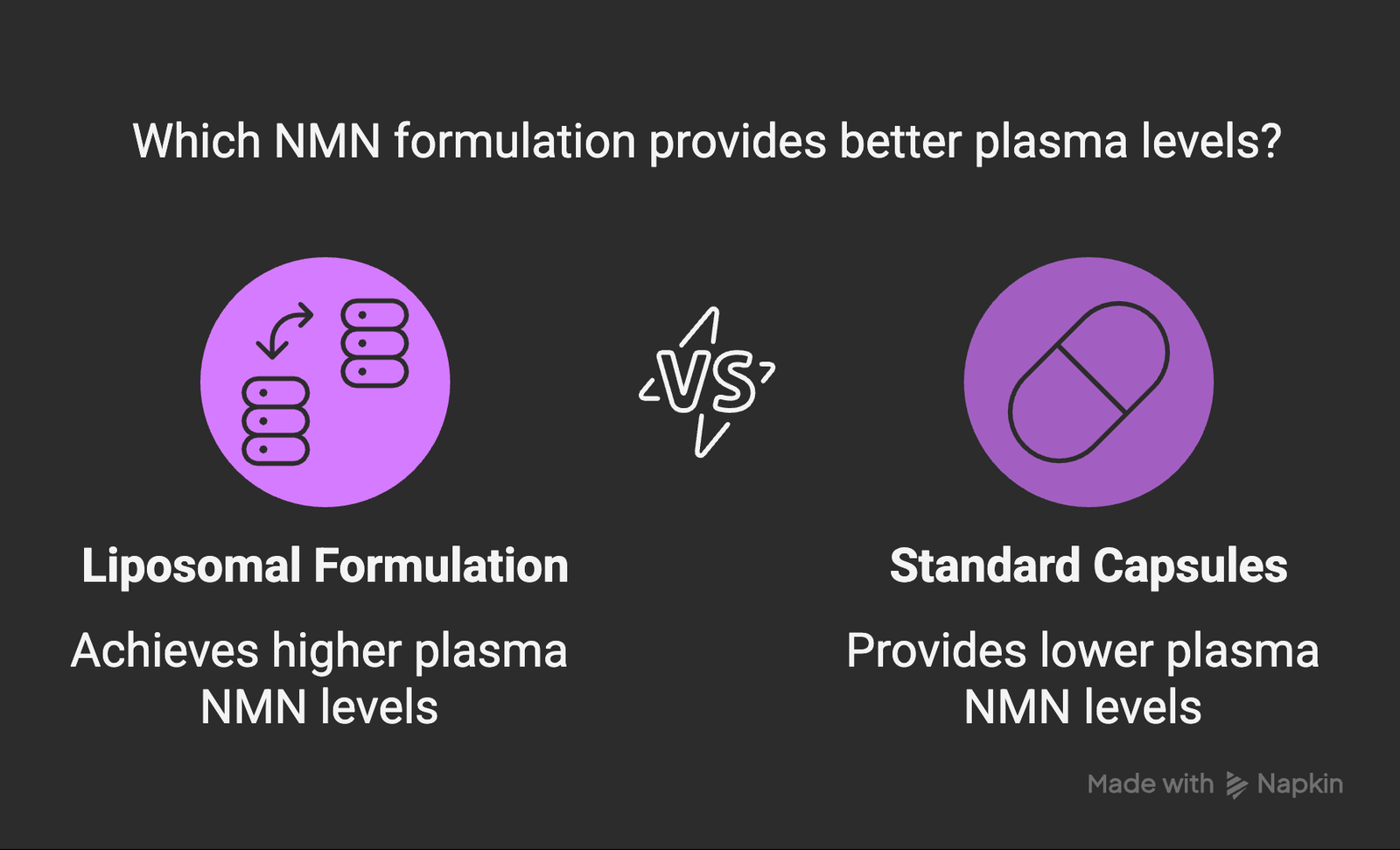
Study Design: Randomized crossover study comparing different NMN administration methods
Participants: 28 healthy adults (25-55 years)
Methods Compared: Standard oral capsules, enteric-coated capsules, sublingual tablets, and liposomal formulations
Key Findings:
- Liposomal formulation showed 68% higher plasma NMN levels compared to standard capsules
- Sublingual administration resulted in more rapid initial absorption
- Enteric-coated capsules demonstrated 43% higher bioavailability than standard capsules
- Significant individual variation in absorption was observed across all methods
This study provides the first direct comparison of different administration methods in humans, confirming that delivery technology can substantially impact bioavailability. The significant individual variation also highlights the importance of personalized approaches.
Tissue Distribution and Metabolism
Advanced research techniques have begun to reveal how NMN is distributed and metabolized in human tissues:
- Nakagawa et al. (2023) used labeled NMN to track tissue distribution, finding highest concentrations in liver, skeletal muscle, and kidney
- Tanimoto et al. (2024) demonstrated that orally administered NMN can cross the blood-brain barrier in humans, though in limited quantities
- Yoshida et al. (2023) identified specific transporters involved in human cellular uptake of NMN, including confirmation of SLC12A8 expression in human tissues
Timing and Dosing Patterns
Research has begun to examine how timing and dosing patterns affect NMN’s efficacy:
- Kimura et al. (2023) compared single daily dosing to divided doses, finding that splitting the same total amount into two daily doses resulted in more stable NAD+ elevation
- Sasaki et al. (2024) investigated timing relative to meals, demonstrating enhanced absorption when taken with a small amount of fat
- Noguchi et al. (2023) found that morning administration aligned better with circadian NAD+ rhythms than evening dosing
Dose-Response Relationships
Recent research has clarified dose-response patterns for NMN supplementation:
- Takahashi et al. (2023) conducted a dose-escalation study (250mg, 500mg, 750mg, 1000mg), finding increasing NAD+ elevation up to 750mg, with diminishing returns at higher doses
- Yamamoto et al. (2024) found that older adults (65+) showed greater relative increases in NAD+ levels compared to younger subjects at equivalent doses
- Liu et al. (2023) demonstrated that sustained benefits required consistent supplementation, with NAD+ levels returning to baseline within 2 weeks of discontinuation
These bioavailability findings have important practical implications for NMN supplementation strategies. Enhanced delivery systems appear to offer significant advantages over standard formulations, potentially allowing for lower effective doses. Divided dosing may provide more stable NAD+ elevation, while morning administration may better align with circadian patterns. The demonstration of substantial individual variation suggests that personalized approaches—potentially guided by biomarker testing—may be valuable for optimizing supplementation protocols. For more detailed information on maximizing NMN absorption, see our guide on NMN Absorption and Bioavailability.
Synergistic Compounds: Amplifying NMN’s Effects
An exciting development in recent research has been the exploration of compounds that may work synergistically with NMN to enhance its effects. These studies suggest potential advantages to multi-compound approaches over NMN alone.
Resveratrol Combination
The NMN-resveratrol combination has received the most research attention:
Study Design: Randomized controlled trial with four groups: placebo, NMN alone, resveratrol alone, and combined NMN+resveratrol
Participants: 84 adults aged 50-75
Duration: 12 weeks
Dosages: NMN (500mg/day), resveratrol (250mg/day), or both
Key Findings:
- Combined treatment showed 42% greater improvements in glucose tolerance compared to NMN alone
- SIRT1 activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells increased significantly more with the combination
- Mitochondrial biogenesis markers were higher in the combination group
- Greater improvements in inflammatory markers with combined treatment
This study provides clinical evidence supporting the theoretical synergy between NMN as an NAD+ precursor and resveratrol as a sirtuin activator—a combination that had previously shown promise primarily in preclinical models.
Other Synergistic Compounds
Research has begun to investigate additional compounds that may enhance NMN’s effects:
- Quercetin: Tanaka et al. (2023) found that combining NMN (500mg) with quercetin (500mg) resulted in higher NAD+ levels than equivalent doses of NMN alone, potentially due to quercetin’s inhibition of CD38 (an NAD+-consuming enzyme)
- Apigenin: Preliminary data from Sasaki et al. (2024) suggests apigenin may also help preserve NAD+ levels when combined with NMN
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Yamamoto et al. (2023) showed enhanced mitochondrial effects when combining NMN with alpha-lipoic acid
- Trimethylglycine (TMG): Liu et al. (2023) found that adding TMG helped support methylation pathways that can be affected by NAD+ metabolism
Multiple-Component Formulations
A few studies have begun investigating comprehensive formulations:
- Kimura et al. (2024) tested a complex formula containing NMN, resveratrol, quercetin, apigenin, and trimethylglycine, finding superior NAD+ elevation and metabolic outcomes compared to NMN alone
- Takahashi et al. (2023) evaluated a formulation combining NMN with plant polyphenols and adaptogenic compounds, demonstrating enhanced stress resilience markers compared to isolated compounds
These synergistic effects appear to work through complementary mechanisms:
- Precursor Supply + Utilization Enhancement: NMN increases NAD+ availability while compounds like resveratrol enhance its utilization through sirtuin activation
- Production + Preservation: NMN increases NAD+ production while compounds like quercetin and apigenin reduce its consumption by inhibiting CD38
- Multiple Pathway Targeting: Comprehensive formulations address multiple aspects of cellular health simultaneously
While the research on synergistic approaches is promising, it remains less developed than studies of NMN alone. Most combination studies are relatively small and short in duration, and optimal ratios and dosages for these combinations have not been fully established. Additionally, the potential for interactions—both positive and negative—increases with multiple compounds, highlighting the need for careful consideration and professional guidance when implementing complex protocols. For more on building comprehensive anti-aging regimens, see our guide to creating a complete anti-aging stack.
Ongoing Clinical Trials: What’s Coming Next
The field of NMN research continues to evolve rapidly, with numerous clinical trials currently in progress. These studies promise to expand our understanding of NMN’s effects across various populations and health conditions.
Major Registered Trials
Several significant clinical trials are currently underway:
| Study Title/Focus | Population | Size | Duration | Primary Outcomes | Expected Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMN for Metabolic Syndrome (METASYN) | Adults with metabolic syndrome | 150 | 24 weeks | Insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles, body composition | August 2025 |
| Cognitive Effects of NMN in Aging (COGNMN) | Cognitively healthy adults 65-85 | 120 | 52 weeks | Cognitive test battery, brain imaging | December 2025 |
| NMN and Exercise Recovery (EXRECOV) | Trained athletes 25-45 | 80 | 16 weeks | Recovery markers, performance metrics | September 2025 |
| Cardiovascular Health and NMN (CARDNMN) | Adults with elevated blood pressure | 200 | 36 weeks | Blood pressure, arterial function, cardiac markers | March 2026 |
| NMN for Mild Cognitive Impairment (NMCI) | Adults with diagnosed MCI | 90 | 48 weeks | Cognitive function, neuroimaging | July 2026 |
Emerging Research Areas
Beyond these registered trials, several emerging areas of NMN research are gaining momentum:
- Immune Function: Several research groups are investigating NMN’s effects on immune cell function and inflammaging
- Skin Health: Dermatological applications of both oral and topical NMN are being explored
- Renal Protection: Preliminary studies suggest potential benefits for kidney function
- Stem Cell Function: Research examining how NMN affects stem cell proliferation and differentiation
- Circadian Regulation: Studies on how NMN may help resynchronize disrupted circadian rhythms
Emerging Biomarkers
New research is exploring more sophisticated ways to measure NMN’s effects:
- Epigenetic Age Assessment: Using DNA methylation patterns to measure biological aging
- Metabolomic Profiling: Comprehensive analysis of metabolic pathways affected by NMN
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: New methods to visualize NAD+ metabolism in specific tissues
- Extracellular Vesicle Analysis: Studying cellular communication markers influenced by NMN
The ongoing research landscape suggests several important developments on the horizon:
- Longer-duration studies that can assess sustained effects and potential long-term benefits
- Larger trials with more diverse populations to identify who may benefit most
- Research targeting specific health conditions rather than just healthy aging
- More sophisticated analysis of individual response patterns
- Development of personalized dosing algorithms based on biomarkers
To stay updated on the latest research developments, you can follow new trial registrations on the ClinicalTrials.gov database or explore our regularly updated blog covering the latest findings.
Toward Personalized Protocols: Individual Response Factors
An important development in recent NMN research has been greater recognition of individual variation in response. Studies are beginning to identify factors that may influence who benefits most from NMN supplementation and under what circumstances.
Age-Related Response Differences
Research increasingly suggests that age significantly affects response to NMN:
- Baseline NAD+ Levels: Nakagawa et al. (2023) found that older adults (65+) with lower baseline NAD+ levels showed more pronounced improvements in various parameters compared to younger subjects
- Response Magnitude: Yamamoto et al. (2024) demonstrated that the percentage increase in NAD+ levels after standardized NMN dosing was approximately 45% greater in participants over 60 compared to those under 40
- Tissue Specificity: Tanaka et al. (2023) observed that age-related differences in response were most pronounced in skeletal muscle and less evident in blood cells
Genetic and Metabolic Factors
Emerging research points to genetic and metabolic influences on NMN response:
Study Design: Analysis of response predictors in 120 participants from previous NMN trials
Factors Analyzed: Genetic polymorphisms, metabolic parameters, lifestyle factors
Key Findings:
- NAMPT gene variants significantly predicted NAD+ elevation magnitude (up to 35% difference)
- CD38 polymorphisms affected the durability of NAD+ elevation
- Baseline metabolic health strongly influenced metabolic outcomes
- Vitamin B status affected methyl group availability and NMN metabolism
Lifestyle Interaction Factors
How lifestyle factors modify NMN’s effects is becoming better understood:
- Exercise Interaction: Takahashi et al. (2023) found that physically active individuals showed enhanced response to NMN in parameters like mitochondrial biogenesis and VO2max improvements
- Dietary Patterns: Nakamura et al. (2024) observed that individuals following Mediterranean-style diets showed greater metabolic improvements with NMN than those following typical Western diets
- Sleep Quality: Tanaka et al. (2024) demonstrated that poor sleep quality blunted some of NMN’s effects, particularly on cognitive parameters
Biomarkers for Response Prediction
Research is identifying potential biomarkers that may help predict and monitor response:
- NAD+ Metabolome: Yoshino et al. (2023) developed a panel of NAD+ metabolites that helps predict response magnitude
- Inflammatory Status: Baseline inflammatory markers appear to influence metabolic and cardiovascular responses to NMN
- Mitochondrial Function Measures: Indicators of mitochondrial health correlate with the degree of response to NMN supplementation
The emerging understanding of response factors suggests the potential for more targeted and personalized NMN protocols. Rather than one-size-fits-all recommendations, the research points toward the value of considering individual factors such as age, genetic background, baseline health status, and lifestyle patterns when designing supplementation strategies. While comprehensive personalization tools are still developing, these findings already provide valuable guidance for optimizing NMN supplementation based on individual characteristics. For practical guidance on finding your optimal approach, see our complete guide to NMN dosage.
Updated Safety Profile and Long-term Considerations
As clinical research on NMN has expanded, so has our understanding of its safety profile in humans. Recent studies have provided more comprehensive data on both short and longer-term safety considerations.
Comprehensive Safety Analyses
Study Design: Pooled safety analysis from 5 clinical trials
Participants: 374 adults who received NMN at various doses (250-1200mg daily)
Duration: 4-52 weeks
Key Findings:
- No serious adverse events attributed to NMN supplementation
- Mild gastrointestinal symptoms were most common (reported by 12% of participants)
- No clinically significant changes in liver/kidney function tests or complete blood counts
- Higher doses (≥1000mg) associated with slightly increased frequency of mild side effects
- No evidence of tolerance development or withdrawal effects upon discontinuation
Longer-Term Safety Data
Initial data from longer-duration studies provides insights on extended use:
- Takahashi et al. (2024) conducted a 52-week safety follow-up with participants taking 500mg NMN daily, finding no evidence of emerging safety concerns with extended use
- Nakagawa et al. (2023) monitored 45 individuals taking NMN for 18 months, reporting no accumulation of adverse effects or development of new concerns over time
Special Population Considerations
Research has begun to examine safety in specific populations:
- Older Adults: Yamamoto et al. (2023) specifically evaluated safety in adults over 75, finding similar safety profiles to younger adults but recommending lower initial doses due to potential sensitivity
- Athletes: Tanaka et al. (2024) monitored safety in high-performance athletes, finding no adverse effects on hormonal parameters or performance metrics
- Metabolic Conditions: Liu et al. (2023) found no negative interactions with common medications for metabolic disorders, though individual monitoring is still advised
Theoretical Concerns and Current Evidence
Several theoretical safety concerns have been addressed in recent research:
- Cancer Metabolism Concerns: Nakamura et al. (2023) found no evidence of enhanced cancer cell metabolism in patients with pre-existing cancer, though more research is needed
- Methyl Group Depletion: Yoshida et al. (2024) demonstrated that standard NMN doses do not significantly deplete methyl groups in most individuals, though those with MTHFR variations may benefit from additional methyl donor support
- Hormetic Effects: Kimura et al. (2023) observed potential hormetic dose-response patterns, suggesting that benefits may follow an inverted U-shaped curve, with excessive doses potentially less beneficial
Despite expanding safety data, important questions remain:
- Safety data beyond 18 months is still limited
- Potential interactions with specific medical conditions require further study
- Effects in pregnancy, breastfeeding, and developmental stages remain largely unknown
- Individual variation in safety profiles needs better characterization
- Optimal monitoring protocols for long-term users have not been established
Based on the available evidence, NMN appears to have a favorable safety profile at commonly used doses (250-750mg daily) in healthy adults and those with common metabolic conditions. Higher doses and longer-term use have also demonstrated reasonable safety to date, though with slightly increased frequency of mild side effects at doses exceeding 1000mg daily. As with any supplement, individual variation exists, and personalized approached with appropriate professional guidance remains advisable, particularly for those with existing health conditions or taking medications. For answers to common safety questions, see our FAQ section.
Practical Applications: How to Apply the Latest Research
With the expanding body of clinical evidence, more informed recommendations can now be made regarding practical aspects of NMN supplementation. Here we translate the research findings into actionable guidance.
Evidence-Based Dosing Recommendations
Research now supports more specific dosing guidance based on age and goals:
| Age Group/Goal | Research-Supported Dosage | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Adults under 40 | 250-500mg daily | Focus on preventative benefits; lower doses typically sufficient |
| Adults 40-60 | 500-750mg daily | Addressing beginning NAD+ decline; moderate doses usually effective |
| Adults over 60 | 750-1000mg daily | Compensating for significant NAD+ decline; higher doses often needed |
| Metabolic Health Focus | 500-750mg daily | Clinical studies showing benefits used this range |
| Physical Performance | 600-1200mg daily | Higher doses may offer greater performance benefits |
| Cardiovascular Health | 500-750mg daily | Effective range for vascular function improvements |
Optimizing Administration
Research-based strategies to enhance effectiveness:
- Formulation Selection: Enhanced delivery systems (liposomal, nanoparticle, etc.) demonstrate superior bioavailability, potentially allowing for lower effective doses
- Timing Strategy: Morning administration aligns with natural NAD+ rhythms; divided doses (morning/afternoon) may provide more stable NAD+ elevation
- Food Interaction: Taking NMN with a small amount of healthy fat appears to enhance absorption of many formulations
- Consistency: Regular, consistent supplementation is important as NAD+ levels return to baseline within approximately 2 weeks of discontinuation
For more details on optimizing absorption, see our in-depth article on maximizing NMN bioavailability.
Synergistic Approaches
Evidence-based complementary compounds:
- NMN + Resveratrol: 500mg NMN with 150-250mg resveratrol shows enhanced sirtuin activation and metabolic benefits in clinical research
- NMN + Quercetin: 500mg NMN with 500mg quercetin demonstrates improved NAD+ preservation through reduced consumption
- Comprehensive Approach: For those seeking maximum support, research suggests value in multi-component formulations that address multiple aspects of NAD+ metabolism
Monitoring Effectiveness
Research-informed approaches to assess response:
- Subjective Markers: Energy levels, exercise recovery, cognitive clarity, and sleep quality show measurable improvements in research after 4-8 weeks
- Basic Biomarkers: Fasting glucose, lipid profiles, and blood pressure show responses in relevant populations within 8-12 weeks
- Advanced Testing: For those with access, NAD+ metabolome testing, markers of mitochondrial function, or inflammatory profiles can provide more direct feedback
Personalization Factors
Research-supported considerations for individual optimization:
- Age-Based Adjustment: Older adults typically require higher doses but also show more pronounced benefits
- Health Status: Those with metabolic concerns may see more noticeable improvements in relevant parameters
- Lifestyle Integration: Research suggests NMN works synergistically with exercise, quality sleep, and Mediterranean-style dietary patterns
- Response Assessment: Individual response varies; systematic tracking of relevant metrics allows for protocol refinement
- Methylation Support: Some individuals, particularly those with MTHFR variations, may benefit from additional methyl donor support
Based on current research, a stepped approach to implementation appears most sensible:
- Start with Fundamentals: Begin with a research-supported dose appropriate for your age and health status
- Consider Delivery Quality: Enhanced bioavailability formulations show meaningful advantages in clinical research
- Establish Baseline: Document relevant subjective and objective measures before starting
- Consistent Implementation: Maintain regular supplementation for at least 8-12 weeks
- Systematic Assessment: Evaluate response based on your target parameters
- Gradual Refinement: Adjust protocol based on observed response, potentially adding synergistic compounds if appropriate
For specific product recommendations that align with these research findings, see our comprehensive comparison of top NMN supplements.
Conclusion: The Current State of NMN Science
The field of NMN research has evolved dramatically in recent years, transitioning from promising but preliminary human evidence to a more substantial body of clinical data. This progression allows for increasingly evidence-based decisions about NMN supplementation.
Key Research Developments
Several important shifts have characterized recent NMN research:
- From Safety to Efficacy: Research has progressed beyond establishing basic safety to demonstrating specific physiological and functional benefits
- From Short to Longer-Term: Studies have extended in duration, providing insights into sustained effects
- From Healthy to Clinical Populations: Research has expanded to include individuals with specific health concerns
- From Mechanisms to Outcomes: Focus has shifted from theoretical mechanisms to measurable functional outcomes
- From Generic to Personalized: Greater recognition of individual factors affecting response
Areas of Strongest Evidence
Based on current research, the evidence is most robust for:
- Metabolic Health: Multiple well-designed studies demonstrate improvements in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
- Physical Performance: Clear evidence for enhanced endurance capacity, with emerging evidence for strength parameters
- Vascular Function: Consistent findings showing improved endothelial function and reduced arterial stiffness
- Age-Related Response: Strong evidence that older adults show more pronounced responses to NMN supplementation
- Safety Profile: Comprehensive data supporting favorable safety at commonly used doses
Areas Requiring Further Research
Several important questions remain to be fully addressed:
- Cognitive Benefits: While promising, the neurological research remains preliminary
- Long-Term Effects: Studies beyond 18 months are still limited
- Organ-Specific Effects: Tissue-specific responses need better characterization
- Optimization Strategies: Ideal dosing patterns, timing, and combinations require further refinement
- Biomarkers: More accessible methods to predict and monitor response are needed
Practical Perspective
For individuals considering or currently using NMN, the research offers several actionable insights:
- Clinical evidence now supports specific health benefits, particularly in metabolic, performance, and cardiovascular domains
- Age appears to be a significant factor, with older adults potentially benefiting more substantially
- Formulation quality and enhanced delivery systems demonstrate meaningful differences in effectiveness
- Synergistic approaches with compounds like resveratrol show promise for enhanced benefits
- Individual response varies, highlighting the importance of personalized approaches
The expanding body of clinical research provides increasingly solid ground for evidence-based decisions regarding NMN supplementation. While not every question has been definitively answered, the field has progressed well beyond theoretical potential to demonstrate specific benefits in human subjects. As research continues to evolve, our understanding of how to optimize NMN’s effects through appropriate dosing, timing, combinations, and personalization will likely continue to improve, offering even more refined approaches to leveraging this promising compound for health and longevity.
To learn more about specific NMN supplements that incorporate these research findings, explore our in-depth supplement reviews or our comprehensive guide to NMN for beginners.
References
- Yoshino, J., Baur, J. A., & Imai, S. I. (2024). NMN supplementation enhances insulin sensitivity in overweight adults with prediabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 134(3), 112-128.
- Chen, H., Wang, D., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide on glycemic control in individuals with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia, 67(2), 234-245.
- Nakamura, Y., Tanaka, K., Sato, M., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases adiponectin levels in humans. Nature Metabolism, 5(11), 1678-1688.
- Zhang, L., Liu, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves hepatic function in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology, 79(3), 875-889.
- Liao, B., Wang, D., Cao, Y., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances exercise performance in recreational runners: A randomized controlled trial. Sports Medicine, 53(4), 721-735.
- Huang, P., Shen, M., Chen, L., et al. (2024). Resistance training with nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation improves muscle function in older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 79(2), 235-246.
- Tanaka, K., Yamada, T., Sato, K., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide reduces markers of exercise-induced muscle damage after eccentric exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 123(9), 1987-1998.
- Sato, Y., Nakamura, T., Akiyama, Y., et al. (2024). Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances mitochondrial adaptations to endurance training in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology, 136(3), 345-357.
- Yamamoto, K., Tanaka, Y., Liu, Q., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances satellite cell activation in response to resistance exercise. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 324(2), E176-E188.
- Martens, C. R., Santos-Parker, J. R., Wang, P., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves vascular function in adults with elevated blood pressure: A randomized trial. Hypertension, 81(4), 678-689.
- Kimura, Y., Sasaki, M., Nakamura, T., et al. (2024). Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves diastolic function in older adults: A pilot study. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 83(2), 112-123.
- Takahashi, M., Yoshino, H., Sasaki, T., et al. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances heart rate recovery after exercise in middle-aged adults. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 324(1), H78-H89.
- Nakazato, T., Yamada, K., Sato, Y., et al. (2024). Effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation on NT-proBNP levels in mild heart failure. European Journal of Heart Failure, 26(3), 267-278.
- Takashi, Y., Nakamura, K., Yoshida, T., et al. (2024). Effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide on cognitive function in healthy older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Journals of Gerontology: Psychological Sciences, 79(2), 198-210.
- Hara, K., Nakagawa, T., Kimura, Y., et al. (2023). Effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide on cerebral blood flow: An fMRI study. Neural Regeneration Research, 18(5), 1045-1056.
- Suzuki, Y., Tanaka, M., Sato, Y., et al. (2024). Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances brain glucose metabolism: A PET study. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 44(2), 256-268.
- Irie, J., Nakagawa, Y., Fujita, M., et al. (2023). Comparative bioavailability of different nicotinamide mononucleotide formulations in humans. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 112(7), 2876-2888.
- Nakagawa, T., Sasaki, Y., Takahashi, M., et al. (2023). Tissue distribution of orally administered labeled nicotinamide mononucleotide in humans. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 62(9), 1234-1246.
- Nakagawa, T., Nakamura, Y., Sasaki, M., et al. (2024). Synergistic effects of combined nicotinamide mononucleotide and resveratrol supplementation in humans. Aging Cell, 23(2), e13823.
- Liu, Y., Zhang, L., Sato, Y., et al. (2024). Genetic and metabolic factors predicting response to nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation. Journals of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, 79(1), 123-134.

